 |
| |
(Coleoptera, Diptera, Hymenoptera and Lepidoptera)
by
Brian Pitkin, Willem Ellis, Colin Plant and Rob Edmunds
|
|
|
|
RORIPPA.
Yellow-cresses. [Brassicaceae]
|
|
Five
species and several hybnrids of Rorippa are recorded in Britain. These include
the Northern Yellow-cress
(R. islandica), Marsh Yellow-cress (R. palustris), Creeping Yellow-cress (R. sylvestris), Great Yellow-cress (R. amphibia) and the Austrian Yellow-cress (R. austriaca) and several hybrids. The BSBI provide a downloadable plant crib for Brassicaceae.
Five British miners are recorded on Rorippa.
A key to the European miners recorded on Rorippa is provided in Bladmineerders van Europa. |

Marsh Yellow-cress
Rorippa palustris
|
Key for the identification of the known mines of British
insects (Diptera and non-Diptera) recorded on Rorippa
|
1a > Leaf and stem mine: Oviposition takes place in the leaf blade where a short mine is
formed until the larva reaches the nearest vein which is then followed
downwards, with the main feeding occurring in the mid-rib, petiole,
or in young plants, also in the stem (Spencer,
1976: 490). Pupation either internal or external.
The
mine begins somewhere in the leaf, generally at the lower surface,
not far from the leaf margin. From there a corridor runs randomly,
until it hits upon a vein. The corridor then follows this vein until
it reaches the midrib. Then the larva starts to bore into the midrib,
and may descend into the petiole or even the stem. Pupation may
take place either within or outside the mine. |
On Brassica, but not yet on Rorippa, in Britain and additional genera of Brassicaceae
elsewhere. Widespread but only recorded from Warwick, Dunbarton
and East Lothian in Britain. Also recorded in the Republic of
Ireland, continental Europe, Egypt, Canada and the U.S.A.
|
Phytomyza
rufipes Meigen, 1830 [Diptera: Agromyzidae]. |
1b > Leaf-miner: A distinctive mine primarily above mid-rib, with irregular short
lateral offshoots into leaf blade. Pupation external (Spencer, 1972:
51 (fig. 172), 55; Spencer, 1976:
270, 271 (fig. 486)).
Branched,
whitish, upper-surface corridor; main axis overlying the midrib;
side branches overlying the main lateral veins. (In Campanula and Phyteuma the mine is much less branched, sometimes nothing
more than a corridor on top of the midrib). Frass in rather long
strings. Usually the mines begins as a long and narrow, shallow,
tortuous lower-surface corridor that ends upon the midrib but otherwise
is not associated with the leaf venation. Often this initial corridor
is filled with callus, and then even less conspicuous. Pupation
outside the mine.
A
linear mine on the upper surface, usually following the midrib and
showing side branches along the veins. The frass is in strings. |
|

Liriomyza strigata larva, lateral
Image: © Willem Ellis (Bladmineerders van Europa)
|
Polyphagous. On more than 40 host genera in 15 families, but not yet on Rorippa, in Britain and elsewhere. Widespread throughout Britain. Also
recorded in the Republic of Ireland. Widespread in continental
Europe.
|
Liriomyza
strigata (Meigen, 1830) [Diptera: Agromyzidae]. |
1c > Leaf-miner: Mine linear, whitish, both upper and lower surface. Pupation internal,
at the end of the mine with the anterior spiracles projecting through
the epidermis (Spencer, 1976:
433). Upper-surface,
less often lower-surface corridor. Frass in isolated grains. Pupation
within the mine, in a, usually lower-surface, pupal chamber. A long whitish upper surface corridor, which eventually goes lower surface. |
|
|
Two
highly polyphagous species of Chromatomyia, with indistinguishable
mines, have been recorded in Britain. These are syngenesiae (Hardy) and horticola (Goureau) which can only be distinguished by the male genitalia. Both species are widespread in Britain and elsewhere, although syngenesiae is almost entirely restricted to Asteraceae. Records on Asteraceae not based on examination of male genitalia are treated in this account as Chromatomyia 'atricornis'.
Chromatomyia horticola is recorded on Rorippa elsewhere but not yet on Rorippa in Britain.
|
Chromatomyia
horticola (Goureau, 1851) [Diptera: Agromyzidae] |
1f > Leaf-miner: Corridor-blotch
mine, normally dorsal; usually whitish; in small leaves it lies
characteristically in the centre of the leaf often touching the
petiole; in larger leaves it lies to one side of the mid-rib. Frass
deposited in green clumps near the leaf margin. Pupation usually
external, sometimes in a separate pupation mine.
Oviposition
whitin the leaf, at the lower surface. The first part of the mine
is a long, sometimes very long, corridor, that mostly will be overrun
by the later developments. Generally this corridor is directed,
frequently guided by a thick vein, to the midrib. The next section
of the mine is large, irregular blotch overlying the basal section
of the midrib. Locally large chunks of midrib tissue are consumed.
From this central blotch excursions are made into the leaf blade:
generally upper-surface, less often lower-surface and locally full-depth.
In plants with narrow leaves, like Diplotaxis, the mine may
occupy the entire width of the leaf. Often several larvae together
in a mine. Frass blackish green, powdery, in clouds, sometimes along
the sides of the corridors, later more in the periphery of the mine
and in the end of extensions of the blotch, sometimes seemingly
absent. (Often the frass can only be seen after the mine has been
opened). Pupation generally in the ground, rarely within he leaf,
in a short mine without frass. Hendel (1928a) described the biology,
larva and puparium.
An initial narrow gallery then leads to a blotch on the midrib of the leaf.
Watch a video of a scaptomyzid fly larva on Arabidopsis on YouTube by mash92587. |
|
|
|
Polyphagous. On
numerous genera of Brassicaceae, Asteraceae, Papaveraceae, Resedaceae,
Tropaeolaceae and Violaceae, including Alliaria, Barbarea, Brassica, Cheiranthus, Cochlearia, Coincyia, Conringia, Diplotaxis, ? Eruca, Erysimum, ? Hesperis. Lepidium, Matthiola, Raphanus, ? Rorippa and Sinapis in Britain. On additional genera of these families and Fabaceae elsewhere. Widespread, from Caithness in the north to Cornwall in the south of Britain. Also recorded in the Republic of Ireland, Europe, the East Palaearctic, Near East and Neartic Region.
|
Scaptomyza flava (Fallén, 1823) [Diptera: Drosophilidae]. |
| 1g > Leaf-miner: Rather small, untidy, full depth, often branched corridor, often close to the leaf margin. Sides irregularly eaten out. Frass in a greyish-green central line that is interrupted from time to time, sometimes partly in strings. In times of rain the frass may run out and appear greenish.
Usually several mines in a leaf. The body is whitish; head greyish brown with Y-shaped lighter marking. Pronotum with a pair of brownish shields. The mandibles have two teeth. |

Mine
of Ceutorhynchus minutus on Raphanus sativus
Image: © Willem Ellis (Bladmineerders van Europa) |
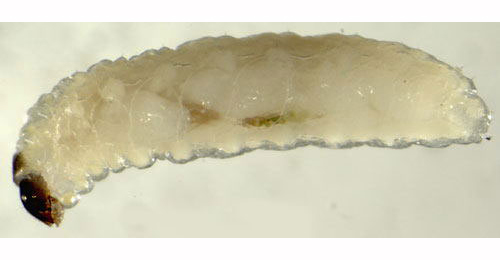
Ceutorhynchus minutus larva, lateral
Image: © Willem Ellis (Bladmineerders van Europa) |
Polyphagous. On numerous genera and species of Brassicaceae, Capparaceae, Resedaceae and Tropaeolaceae, but not yet on Rorippa, in Britain and numerous Brassicaceae elsewhere. Widespread in Britain and continental
Europe. Also recorded in the Republic of Ireland.
|
| Ceutorhynchus
minutus (Marsham, 1802) [Coleoptera: Curculionidae]. |
|
|




