|
||||||
|
ANTHYLLIS. Kidney Vetch. [Fabaceae] |
|
|
Kidney Vetch (A. vulneraria), is the only native species of Anthyllis recorded in Britain. There are several native and introduced subspecies including the introduced species including Bladder Vetch (A. tetraphylla). The BSBI provide a downloadable plant crib for Anthyllis. Eleven British miners are recorded on Anthyllis. A key to the European miners recorded on Anthyllis is provided in Bladmineerders van Europa. |
|
Key for the identification of the known mines of British |
Note: Diptera larvae may live in a corridor mine, a corridor-blotch mine, or a blotch mine, but never in a case, a rolled or folded leaf, a tentiform mine or sandwiched between two more or less circular leaf sections in later instars. Pupation never in a cocoon. All mining Diptera larvae are leg-less maggots without a head capsule (see examples). They never have thoracic or abdominal legs. They do not have chewing mouthparts, although they do have a characteristic cephalo-pharyngeal skeleton (see examples), usually visible internally through the body wall. The larvae lie on their sides within the mine and use their pick-like mouthparts to feed on plant tissue. In some corridor miners frass may lie in two rows on alternate sides of the mine. In order to vacate the mine the fully grown larva cuts an exit slit, which is usually semi-circular (see Liriomyza huidobrensis video). The pupa is formed within the hardened last larval skin or puparium and as a result sheaths enclosing head appendages, wings and legs are not visible externally (see examples). See Key to non-Diptera. |
1a > Leaf-miner: Linear mine in sepals and leaves (Spencer, 1972b: 88, as vulnerariae ; Spencer, 1990: 125). A corridor, largely lower-surface, often following a vein. In the end a short upper-surface corridor or small blotch. Pupation outside the mine. |
|
Phytomyza brischkei Hendel, 1922 [Diptera: Agromyzidae]. |
1b > Leaf-miner: Mine in leaf. |
2a > Leaf-miner: A distinctive mine primarily above mid-rib, with irregular short lateral offshoots into leaf blade. Pupation external (Spencer, 1972: 51 (fig. 172), 55; Spencer, 1976: 270, 271 (fig. 486)). Branched, whitish, upper-surface corridor; main axis overlying the midrib; side branches overlying the main lateral veins. (In Campanula and Phyteuma the mine is much less branched, sometimes nothing more than a corridor on top of the midrib). Frass in rather long strings. Usually the mines begins as a long and narrow, shallow, tortuous lower-surface corridor that ends upon the midrib but otherwise is not associated with the leaf venation. Often this initial corridor is filled with callus, and then even less conspicuous. Pupation outside the mine. A linear mine on the upper surface, usually following the midrib and showing side branches along the veins. The frass is in strings. |
|
Liriomyza strigata (Meigen, 1830) [Diptera: Agromyzidae]. |
2b > Leaf-miner: Corridor leaf-mine in leaves. An upper surface linear mine with frass in conspicuous greenish strips, largely alternating at each side of the channel (Spencer, 1976: 241). Upper-surface, unbranched corridor, relatively broad from the start on, but only weakly widening subsequently. The fresh mine is bright green, but turns whitish, later brown, quickly. Frass in a wide green band in the centre of the corridor, with small black granules at either side. Pupation outside the mine. Forms an upper surface mine, with the frass in a green strips. |
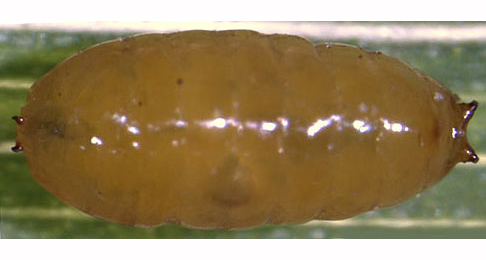 Liriomyza congesta puparium Image: © Willem Ellis (Bladmineerders van Europa) |
|
Liriomyza congesta (Becker, 1903) [Diptera: Agromyzidae]. |
2c > Leaf-miner: A narrow linear mine adjoining the leaf margin in the first instar, which later develops into an irregular blotch with conspicuous lumps of greenish frass (Spencer, 1976: 302). The first instar larva makes a narrow upper-surface corridor along the leaf margin. After it has moulted it begins a large upper-surface blotch. Frass in conspicuous green lumps, that can run out irregularly. Pupation outside the mine. Forms a narrow linear mine by the margin of the leaf which later develops into a blotch. The blotch has clumps of greenish frass. |
|
Phytoliriomyza variegata (Meigen, 1830) [Diptera: Agromyzidae]. |
2d > Leaf-miner: A short, irregular, linear upper surface mine on any part of the leaf. Also recorded from young pods (Bland, 1997a). Long corridor mine. As a rule the first part of the mine is lower-surface, the later part upper-surface. Often the loops are so dense that a secondary blotch is the result. Because upper- and lower-surface corridor segments often cross, the mine obtains a strange array of transparant patches. There is no association with the midrib. Frass in strings and thread fragments. Pupation outside the mine; exit slit in upper epidermis. Mine not associated with the veins or midrib of the leaf (It is this character which enables distinction from another Agromyzid pest species - Liriomyza huidobriensis). The larvae may leave one leaf (if not large enough) and enter another leaf, via the petiole). It exits the leaf to pupate through a semi-circular slit in the upper surface of the leaf. |
|
Liriomyza bryoniae (Kaltenbach, 1858) [Diptera: Agromyzidae]. |
2e > Leaf-miner: The mine starts as a long, narrow, winding corridor running towards the midrib, widening to a blotch. Usually upper-surface, but in small leaves also full-depth parts may occur. The blotch has broad lobes; in their ends most frass is accumulated in the form of green patches or clouds. Sometimes several larvae share mine. Pupation usually in the soil, less often in the leaf (and then generally not in the mine itself but in a small separated mine, that may even be made in the petiole). |
 Mine of Scaptomyza graminum on Cerastium glomeratum Image: © Jean-Yves Baugnée (Bladmineerders van Europa) |
|
Scaptomyza graminum (Fallén, 1823) [Diptera: Drosophilidae]. |
2f > Leaf-miner: Corridor-blotch mine, normally dorsal; usually whitish; in small leaves it lies characteristically in the centre of the leaf often touching the petiole; in larger leaves it lies to one side of the mid-rib. Frass deposited in green clumps near the leaf margin. Pupation usually external, sometimes in a separate pupation mine. Oviposition whitin the leaf, at the lower surface. The first part of the mine is a long, sometimes very long, corridor, that mostly will be overrun by the later developments. Generally this corridor is directed, frequently guided by a thick vein, to the midrib. The next section of the mine is large, irregular blotch overlying the basal section of the midrib. Locally large chunks of midrib tissue are consumed. From this central blotch excursions are made into the leaf blade: generally upper-surface, less often lower-surface and locally full-depth. In plants with narrow leaves, like Diplotaxis, the mine may occupy the entire width of the leaf. Often several larvae together in a mine. Frass blackish green, powdery, in clouds, sometimes along the sides of the corridors, later more in the periphery of the mine and in the end of extensions of the blotch, sometimes seemingly absent. (Often the frass can only be seen after the mine has been opened). Pupation generally in the ground, rarely within he leaf, in a short mine without frass. Hendel (1928a) described the biology, larva and puparium. An initial narrow gallery then leads to a blotch on the midrib of the leaf. Watch a video of a scaptomyzid fly larva on Arabidopsis on YouTube by mash92587. |
|
Scaptomyza flava (Fallén, 1823) [Diptera: Drosophilidae]. |
2g > Leaf-miner: Larva producing a short narrow linear mine not associated with the margin, which then develops into a conspicuous white blotch centred on the mid-rib. At the end of feeding the larva lies for one or two days along the mid-rib. Pupation external (Spencer, 1972b: 37 (fig. 114b); Spencer, 1976: 126, fig. 213A). Broad and short hook-like upper-surface corridor, ending in a little blotch in the centre of a leaflet. The blotch is upper-surface as well, but has some deep spots, giving the mine a mottled appearance when hold against the light. Frass in the blotch in a few large lumps. Pupation outside the mine. A short, broad gallery leading to a conspicuous, roundish white blotch in the centre of the leaf. The blotch is upper surface with full depth spots - comprising of large clumps of frass. Puparium reddish |
|
Agromyza nana Meigen, 1830 [Diptera: Agromyzidae]. |
|
Key for the identification of the known mines of British |
|
Note: The larvae of mining Coleoptera, Hymenoptera and Lepidoptera may live in a corridor mine, a corridor-blotch mine, a blotch mine, a case, a rolled or folded leaf, a tentiform mine or sandwiched between two more or less circular leaf sections in later instars. Larva may pupate in a silk cocoon. The larva may have six legs (although they may be reduced or absent), a head capsule and chewing mouthparts with opposable mandibles (see video of a gracillarid larva feeding). Larvae of Hymenoptera and Lepidoptera usually also have abdominal legs (see examples). Frass, if present, never in two rows. Unless feeding externally from within a case the larva usually vacates the mine by chewing an exit hole. Pupa with visible head appendages, wings and legs which lie in sheaths (see examples). |
1a > Leaf-miner: The first generation initially forms an unmistakable leaf-mine on Anthyllis vulneraria, but the second generation feeds on the flowers. Feeding signs on other plants vary in appearance. Larvae can move between sewn leaves, and more than one larva may be found together. Larvae in a small full depth blotch, often with extensions. Frass concentrated in one corner of the mine. The mining activities may cause the leaf to roll inwards. Older larvae live free among spun leaves, but still they may make then full depth mines by feeding on the leaf tissue from a small opening. |
 Aproaerema anthyllidella larva, dorsal Image: © Steve Wullaert (Bladmineerders van Europa) |
|
Aproaerema anthyllidella (Hübner, 1813) [Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae]. |
1b > Leaf-miner: In the first instar the larva mines the leaves, forming short, irregular, blotch-like mines, but in later instars it lives externally, feeding in spun leaves and often twisting those of tender shoots. Larval head light-brown or yellowish brown, edged with black postero-laterally, ocellar area blackish; prothoracic plate black edged with whitish anteriorly; abdomen dull dark green; pinacula distinct, black, sometimes brownish but with black bases to setae; anal plate large, black (Bradley et al., 1973). Small, full depth mine without a definite shape; little frass. Some silk is deposited in the mine. The larva soon leaves the mine and continues feeding among spun leaves. |
|
Cnephasia incertana (Treitschke, 1835) [Lepidoptera: Tortricidae]. |
1c > Leaf-miner: Oviposition on the leaf underside. The mine begins as a long corridor with a very broad, green frass line. This corridor suddenly widens into a broad blotch, that in the end may occupy almost an entire leaflet. The blotch generally begins in the leaf base, and it is here that most frass is concentrated. Shortly before pupation the larva leaves its mine through an exit slit in the lower epidermis. After the mine has been vacated the leaflet drops off. |
|
Trifurcula cryptella (Stainton, 1856) [Lepidoptera: Nepticulidae]. |
| Last updated 30-Jun-2019 Brian Pitkin | ||

